What is Learning and Development?
Let's start with the basics and understand what is learning and development. Quite simply, learning and development refers to the process of improving an employee's skill, knowledge, and competency. The term comprises of two components:
Thank you for downloading!
P.S. - Don’t forget to check your spam folder,
if you don’t find the email in your primary email.

A. Learning: It signifies the acquisition of skills, knowledge, and attitudes through experience and teaching.
B. Development: It signifies the deepening of knowledge with respect to the employee's personal and organizational development goals. It is relatively long-term in approach.
The end goal of L&D is to
- enhance individual/group performance and efficiency,
- drive behavioral change within the individual/group in the organization.
- share knowledge and insights to supercharge employee performance, and
- build a culture of holistic workplace learning.
The pandemic has transformed nearly every sector—Human Resources and L&D are not exceptions.
Here's why learning and development is increasingly becoming important in the current employee
development landscape.
-
Skill-building is becoming common-place: Did you know that Amazon is investing
over $700M to provide upskilling training to their employees? Furthermore, according
to a recent
Udemy report,
38% of the workforce was upskilled in 2020. Another
McKinsey report
claims that for 69% of respondents, their organizations are engaging more in skill-building
now than they did before the COVID-19 crisis began. The primary factor driving this change?
The immediate need to close the skills gap. In fact, the report suggests that around 62% of
organizations consider skill development to be one of the top three goals for L&D programs.
-
Skill requirements are fast-changing: COVID-19 is accelerating the need
for new workforce skills as suggested by the McKinsey Report. With the surge in
digitization and remote work, employees need to exhibit a slew of new skills to
adapt to and support the "new" workforce. Interestingly, the new must-have
skills that emerged on top were social and emotional skills such as:
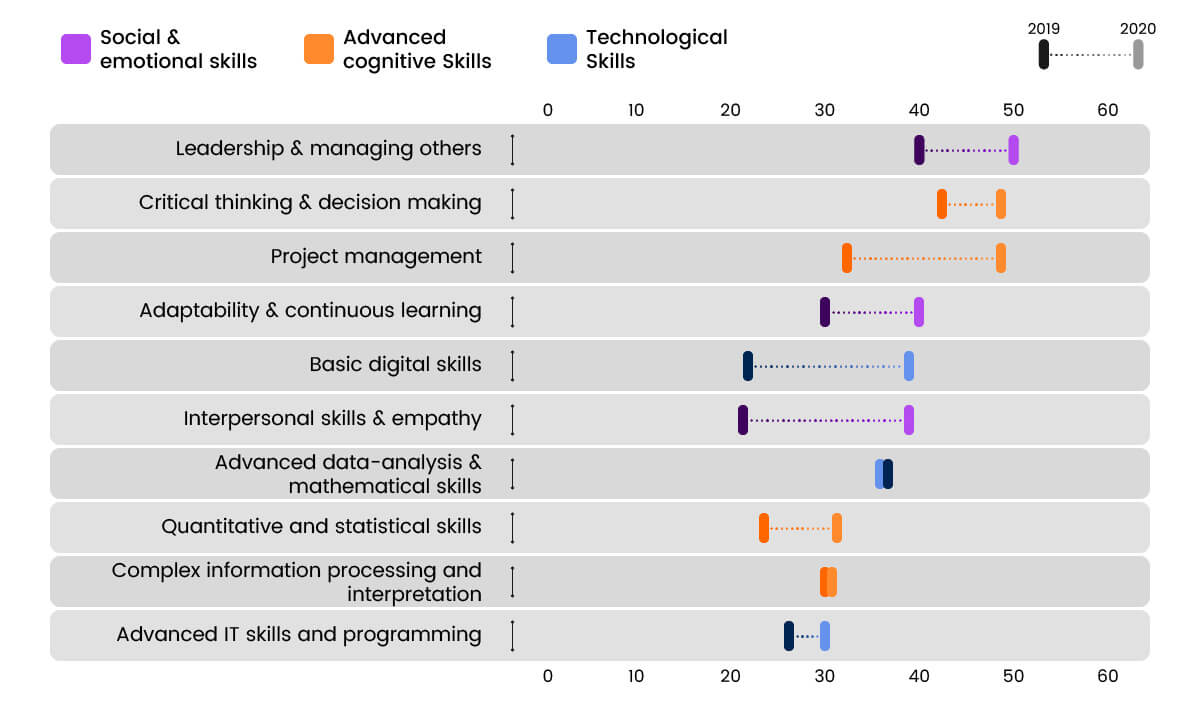
- Empathy and inter-personal (particularly in the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors)
- Leadership
- Adaptability
- Critical-thinking
- Decision-making
- Project management
In other words, "softer" and more "advanced" cognitive skills are taking center stage. Additionally, basic digital skills have also become a raging priority for obvious reasons since the pandemic began.
-
Need for redeploying talent to new roles: 46% of respondents claim that
there has been an increase in redeploying talent at their respective organizations.
Moreover, a LinkedIn survey indicates that "learners without the obvious skills
adjacencies are making the leap into emerging roles." In simpler words, employees
who have moved into "emerging roles" over the past five years came from entirely
different occupations. For instance, half of the employees who moved into data
science and artificial intelligence (AI) roles came from unrelated industries.
The same is true for engineering roles (67%), content roles (72%), and sales (75%).
Moreover, people who transitioned into data and AI
had the largest variation in skill profiles, with half of them possessing skills with low similarity. Clearly, the need for L&D is no longer a one-time investment. Organizations will continually need to regroup to understand the degree of skill-building required as the workplace demands change.
Now that we've understood how integrally tied skill-building is to learning and
development initiatives, let's look at the top 3 skills employees must ace as stated in
the latest LinkedIn survey. According to the survey, the following "power" skills are
critical to future-proofing employees and helping them thrive in a competitive workplace
going forward:
-
Resilience and adaptability: Organizations are increasingly looking for employees who can flex their resilience muscles as needed. This is where learning plays a critical role as 60% of employees surveyed globally reported that learning makes them more capable of adapting to change.
-
Technology skills/digital fluency: For an employee to qualify as being digitally fluent, they
need to have the requisite technology skills to effectively operate in an increasingly digital world.
From Microsoft Office skills to advanced Artificial Intelligence capabilities, employees must be proficient
across the spectrum.
-
Communication across remote or distributed teams: Enterprises are also on the lookout for employees who can easily work and collaborate in a virtual working environment.
Other skills that made to the top 10 list include:
- Emotional intelligence
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Leading through change
- Change management
- Dealing with stress/being more mindful
- Time management
- Creativity
Additionally, the survey also highlights the fastest-growing top 5 skills in the
business, sales, IT, and engineering domains. These include:
- Business: Customer Experience, Digital Marketing, Data Analysis, Financial Statements, Forecasting, and Analytical Skills
-
Sales: Data Analysis, Technical Support, Customer Relationship Management, Sales Process, and Consulting
-
Information Technology: Cybersecurity, Network Engineering, Analytical Skills, Scrum, and Information Security
-
Engineering: React.js, Docker, AWS, Node.js, and MongoDB
In Summary: In 2022, Learning and Development will involve enhancing the effectiveness of organizations and improving individuals' performance by focusing on skill-building and redeploying talent into new roles. When it comes to understanding what is L&D and embracing its essence, enterprises need to remember that
One, it has emerged as a "need-to-have" as opposed to being a nice-to-have component for
employee development.
Two, they need to double down on their efforts to upskill or reskill employees if they
wish to close the ever-widening skills gap.
Three, they need to align their L&D strategy with the organizational goals and reshape
the way their enterprise operates in 2022.





